Sunlight is perhaps the element that keeps us all healthy and energetic.
However, in relation to growing food, its direct exposure can be detrimental. This is because solar radiation can damage plants.
Cultivated plants need a constant supply of light to thrive. When direct sunlight is exceeded, high ultraviolet rays can cause significant damage to the health of a crop. This damage can range from deregulation of photosynthetic production to sunburn, which can be extremely severe.
In addition, ultraviolet rays can also be harmful to pesticides, pest and parasite defenses, which are essential to maintaining a healthy crop. When ultraviolet light exceeds the tolerance level of chemicals, these resources cannot function properly and the crop is more vulnerable to pests.
Too much direct sunlight can also disrupt the natural pattern of crop development. When there is an overproduction of light, the plant can enter a state of stress and reduce its growth rate. This can happen even when the water supply is adequate. The result is an inferior crop resulting in a significant reduction in profitability for growers.
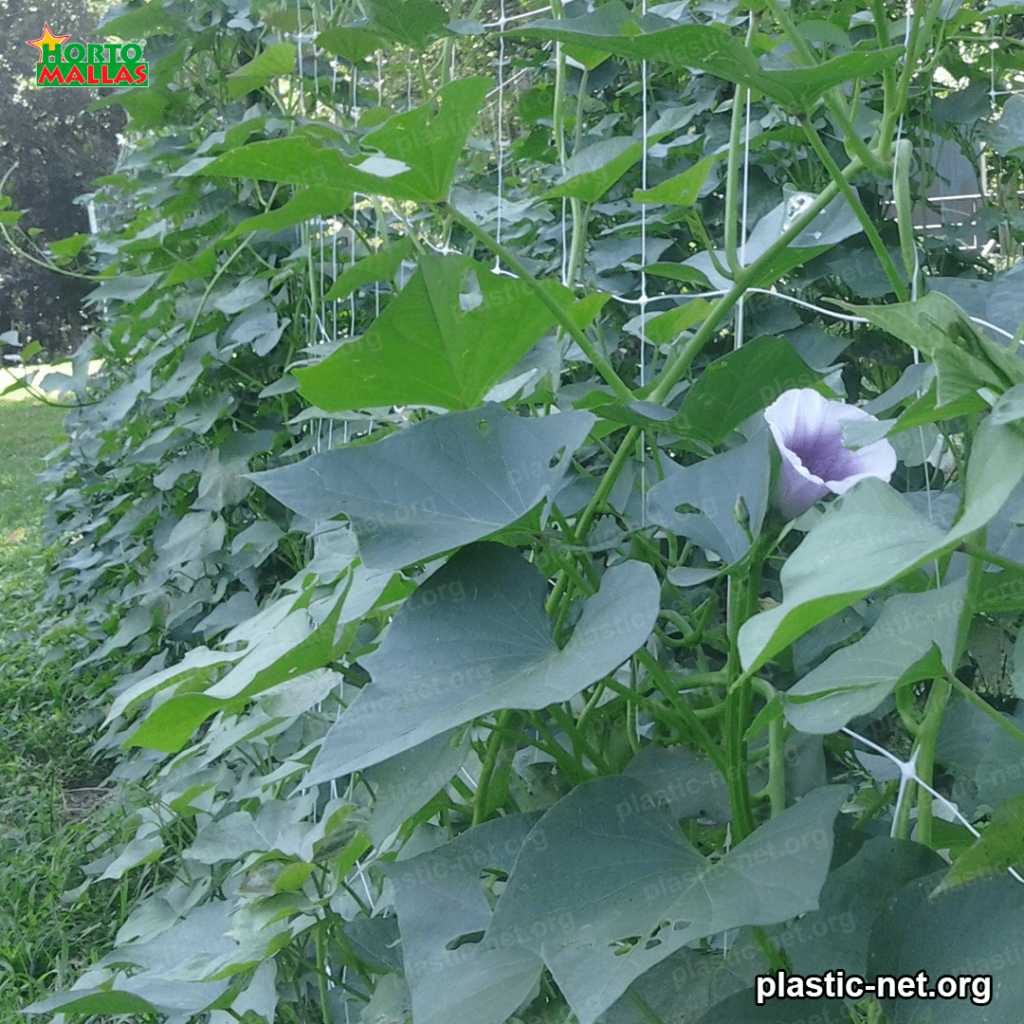

Equally important is the amount of heat produced by the sun.
This can cause dehydration of a crop, resulting in yellow leaf spots, reduced growth rate, increased sensitivity to chemicals, and ultimately a poor crop.
Too much direct solar radiation can be extremely damaging to an agricultural crop. To avoid these negative effects, farmers can join together to strengthen the resilience of their crops. For example, they can use modern technologies and practices to reduce the harmful effects of the sun. This can include the installation of solar panels, improved farmland and the construction of subway farms. From using filters to creating sustainable farming practices, farmers can help their crops thrive under much healthier conditions. They can also implement land use models that best suit their particular needs.
Funding and research also play a key role in combating the damage the sun can cause to food production. Governments and organizations worldwide conduct research projects to improve soil quality and develop resistance to ultraviolet light. These communities do incredible work to identify sustainable solutions that can increase food supply without exposing crops to sun damage.
It is important to avoid exposing an agricultural crop to direct sunlight to protect against the significant damage this exposure can have. Además, debemos señalar que mediante el uso de tecnologías adecuadas, financiamiento y prácticas agrícolas sostenibles, podemos implementar soluciones efectivas que ayuden a los agricultores a mejorar la rentabilidad de sus cultivos sin comprometer la salud y calidad de los mismos
Sun damage to agricultural crops
Agricultural plants are prone to various damages and mistreatments caused by excessive sunlight. Sunlight is one of the basic factors for photosynthesis, but as with air, water and nutrients, excess amounts can cause premature death or alterations in plant growth or development.
The most common sun damage to agricultural crops is leaf scorch, consisting of brown spots and dulling of green tissue. This occurs when crops face inadequate solar exposure, experience drought or water stress, or when irrigation or enrichment systems cannot maintain stable plant growth.Combining these climatic effects with dehydration leads to the loss of texture in the tissues, causing their softening and in turn their early decomposition.
In addition, excess solar energy on agricultural crops contributes to desiccation and desquamation of leaves, separating tissue cells and causing a velvety feel. Likewise, excess sunlight can cause a lack of nutrients in crops due to the rise in temperature and thus evaporation, in addition to affecting germination and establishing a disadvantage for crops.
This sun damage to agricultural crops is especially detrimental during winter periods, especially when extreme cold often causes crops to have trouble absorbing the sunlight required for their well-being, allowing the strength of the sun’s rays to damage their structures. This is especially damaging to plants in the same way as winds, as both elements combine to tire leaves and have a lethal effect on crops.
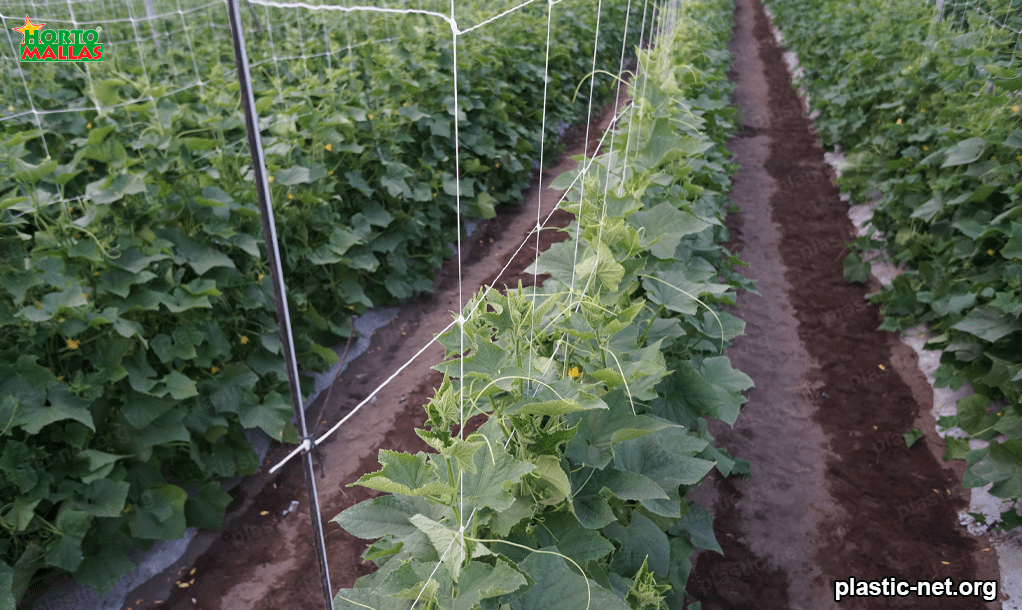

There are some preventive measures to protect agricultural crops when the sun becomes too intense sunlight.
For example, modifying the density of nearby trees, extending roofs and installing irrigation systems can mitigate the damaging effects of the sun while increasing crop yields.
Wild agricultural crops must also receive adequate attention to avoid sun damage, especially since these plants do not have access to basic services such as irrigation or enrichment, so it is necessary to make them have a defense against the harmful effects of sunlight. Natural irrigation can also remedy some of this damage, as can applying pesticides and fertilizers to fields.
Whether farmers are personally managing or controlling crops, the agricultural industry must keep in mind the potential harm that excessive sunlight can inflict on crops and take immediate action to rectify the situation upon detection. These measures are necessary to guarantee the production, quality and quantity of the crop, it is necessary to take care of the plants and the impact that the sun can have on them. The best way to regulate the damage caused by excess sunlight on agricultural crops is to gradually adapt them to solar dependence, thus avoiding destructive effects on vegetative cycles.
How to avoid damage to an agricultural crop by using shade netting
Shade netting is an excellent way to prevent damage to the agricultural crop. Shade netting provides an optimal environment and conditions for optimized crop growth. The shade netting provides sufficient amount of sunlight so that the best results can be obtained. This shade is also very useful in limiting the rate of water evaporation, providing optimal conditions for germination. Shade netting also regulates the climate, preventing the formation of fires, which are considered detrimental to crops.
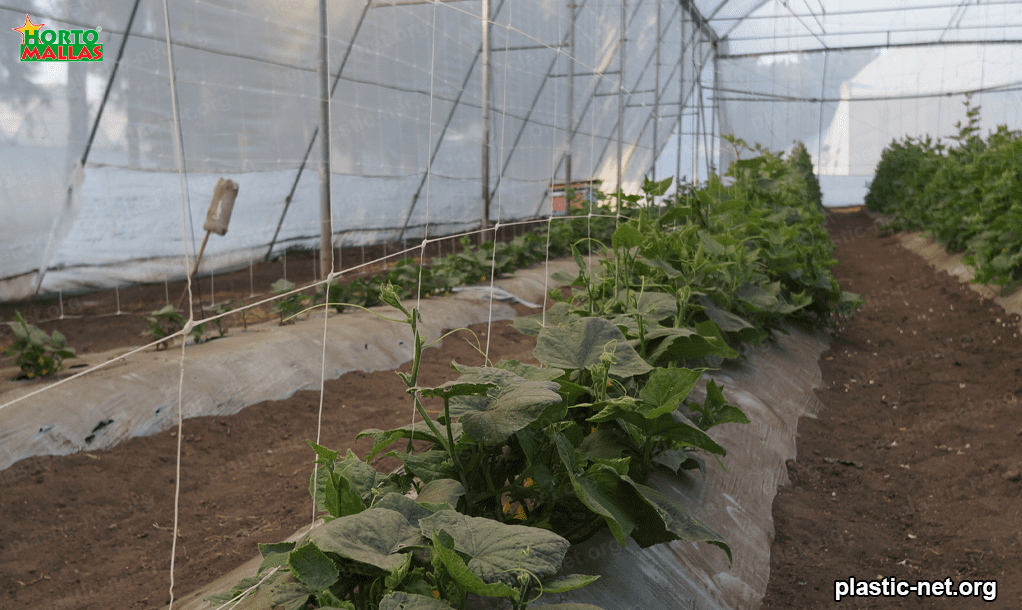

In addition to the ability to reduce exposures to inadequate shade conditions, shade netting can also prevent damage to the natural soil due to ultraviolet radioscopy
providing a safer environment and conditions for the crop. This is especially useful for crops that require a lot of sunlight, such as floristry, fruit and vegetable production, as well as poultry farming.
Shade netting provides the horticulturist with the ability to control sunlight content, which helps regulate temperature and can prevent dehydration of their crops. can be extremely useful for fruit production, as it helps establish a proper balance between fruit production and fruit quality.
Shade netting also prevents sun glare, providing a glare-free environment that helps prevent crop scorch. is also an excellent way to retain moisture. This feature is essential for the production of ripe fruit. Once the fruit ripens, it is important that the shade netting retains adequate moisture, thus ensuring that the fruit remains fresh and edible, Avoiding crop damage from wind. Wind conditions can sometimes be very strong, and this can seriously damage crops. For example, wind can spread pollen, affect crop flowering, and even blow fruit off the plant. Shade netting reduces the impact of wind, limiting crop damage.
Shade netting provides an excellent balance between sunlight and the protection needed to obtain the best crop results. This is achieved through the amount of sunlight achievable, as well as insulation against adverse environmental factors. This allows growers to achieve the optimum in crop creation. Shade netting is truly one of the best tools for the prevention of damage to the agricultural crop, and should be considered as an excellent way to obtain the best results.